By Dr Jatin Patel
History
A 59 year old woman presented with ongoing lateral ankle pain for many years, with the pain having increase over the past two years.
Imaging
X- Ray and CT
Findings
X-Ray
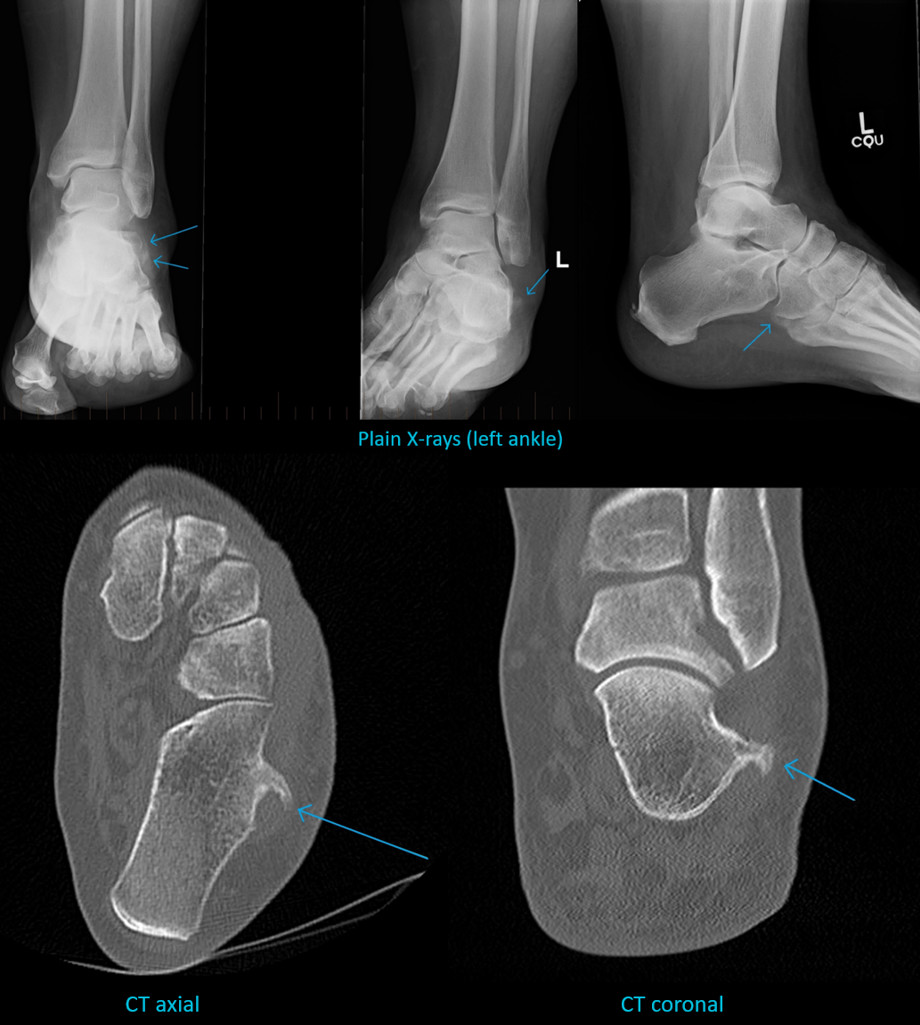
On the AP view of the ankle, a bony irregularity adjacent to the lateral border of the calcaneum/cuboid can be seen. This is more prominent from older films and may be an old avulsion fracture at this site. CT was suggested for further evaluation.
CT
There is a hypertrophy of the peroneal tubercle with an osteochondroma-like projection measuring 15mm in length. This protrudes in between the peroneal tendons and results in marked peroneal tenosynovitis. This hypertrophy corresponds to the abnormality seen on the previous X-ray.
Diagnosis/Management
Peroneal tubercle hypertrophy with associated marked peroneal tenosynovitis.
Two bony projections or protuberances can be seen along the lateral wall of the calcaneus, viz: the peroneal tubercle and the retrotrochlear eminence.
The retrotrochlear eminence is located posterior to the peroneal tubercle and the peroneal tendons. It may be prominent in those with a prominent peroneus quartus muscle (an accessory peroneal muscle).
The peroneal tubercle is present inferior to the lateral malleolus, located in between the peroneal longus and brevis tendons and separating them. The common synovial sheath covering the two tendons proximal to the tubercle divides into two slips to individually enclose the peroneal longus and brevis tendons at the tubercle and distal to it. The peroneus brevis is superior to the tubercle and the peroneus longus is inferior to the tubercle. An enlarged peroneal tubercle can impinge upon the peroneus tendons and result in tenosynovitis. Occasionally an adventitial bursa can develop over the tubercle due to repeated friction, which in turn may become symptomatic.
The initial management of the condition is conservative but surgical resection of the tubercle may be required in those who are not responding to conservative management.